

Britannica Beyond We’ve created a new place where questions are at the center of learning.
#Dispersio of light how to#
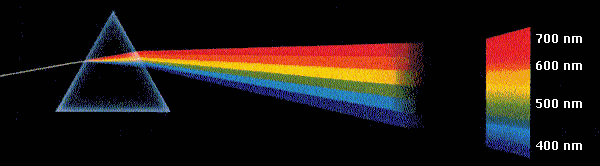
COVID-19 Portal While this global health crisis continues to evolve, it can be useful to look to past pandemics to better understand how to respond today.Student Portal Britannica is the ultimate student resource for key school subjects like history, government, literature, and more.This Time in History In these videos, find out what happened this month (or any month!) in history.#WTFact Videos In #WTFact Britannica shares some of the most bizarre facts we can find.Demystified Videos In Demystified, Britannica has all the answers to your burning questions.Britannica Explains In these videos, Britannica explains a variety of topics and answers frequently asked questions.Britannica Classics Check out these retro videos from Encyclopedia Britannica’s archives.It is not perfect, but the departure from perfect focus forms what is called the "circle of least confusion". For a lens with spherical aberration, the best approximation to use for the focal length is the distance at which the difference between the paraxial and marginal rays is the smallest. The simplest way to explain dispersion is through dispersion in the prism. The use of the lens equation likewise presumes an ideal lens, and that equation is practically true only for the rays close to the optic axis, the so-called paraxial rays. What is Dispersion of Light When white light is passed through a glass prism it splits into its spectrum of colours (in order violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red) and this process of white light splitting into its constituent colours is termed as dispersion. When the concept of principal focal length is used, the presumption is that all parallel rays focus at the same distance, which is of course true only if there are no aberrations.

The use of symmetric doublets like the arthroscopic doublet greatly reduces spherical aberration. For multiple lenses, spherical aberrations can be canceled by overcorrecting some elements. But when it passes through a rectangular glass slab no color is seen.ĭispersive power can be defined as the relative change in the focal length of a lens$\frac$įor lenses made with spherical surfaces, rays which are parallel to the optic axis but at different distances from the optic axis fail to converge to the same point, For a single lens, spherical aberration can be minimized by bending the lens into its best form. Which figure shows the correct light colour (s) after passing through prism Reveal Answer 2. Three light rays: one red, one blue and one green fall on a glass prism as shown in the figure. Hence, when a ray of white light is passed through a glass prism, it is dispersed into different colors. Physics Revision Questions for Dispersion of Light 1. But at the second face of the prism, the dispersion is opposite to that of the first face and equal in magnitude, so they cancel each other and the light emerging from second face of slab is white. When white light enters into a rectangular glass slab, it is dispersed at the first face by first prism.

But when it is passed through a rectangular glass slab no color is seen as it behaves as combination of two prism of same refractive index attached in opposite manner to each other. When a ray of light is passed through a glass prism it get dispersed because the different colors of light are deviated in different amount. Thus violet light will be deviated more and lies outwards bottom where as red light deviated less towards top of the spectrum. The deviation produced by prism is δ = (μ -1) A, where μ is refractive index of material of the prism and A is angle having more wavelengths ids deviated least than the violet light. The dispersion occurs due to refraction because the white light has to travel in the glass medium to disperse whereas the mirror is an opaque object. The cause of dispersion of light is due to the variation of the refractive index of the medium with color of light.Ī substance in which waves of different frequencies travel at different speed is known as dispersive medium


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
